In this tutorial, you’ll see how to watch real time TCP and UDP ports on Linux. In Linux each service running use a particular protocol (TCP/UDP) and a port on which communication happens with other processes/Service. So In this article, we’ll show you how you can monitor running TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) or UDP (User Datagram Protocol) ports in real-time.
Commands to view all open ports on the Linux system:
- netstat
- ss
Note: netstat command is deprecated and ss command is used nowadays which shows more detailed network stats.
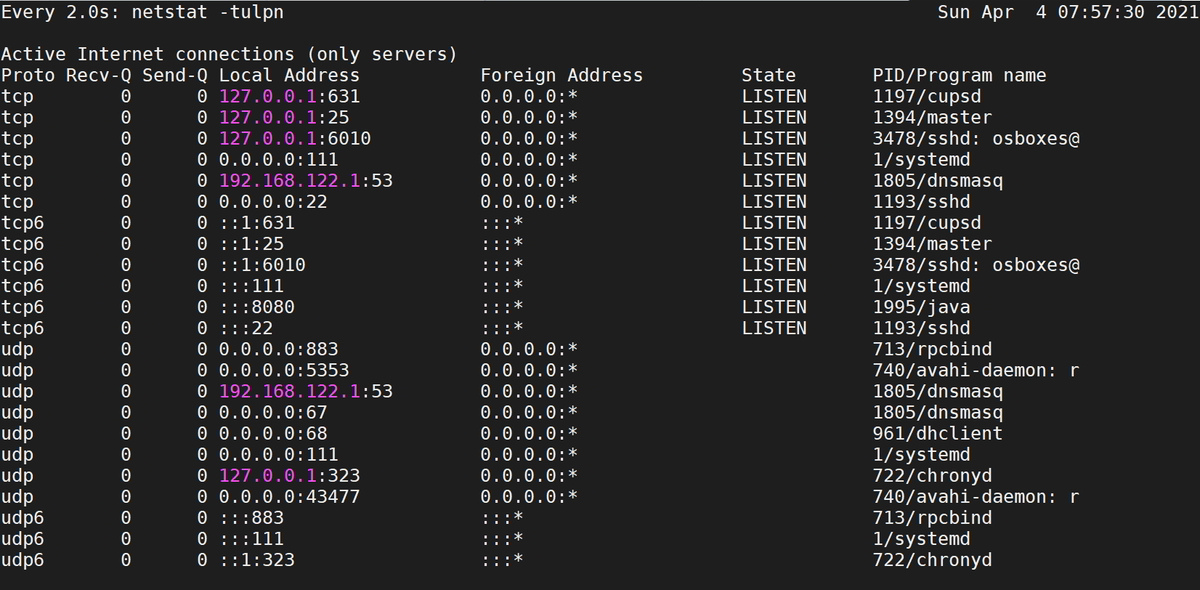
For Command ” sudo netstat -tulpn “

Sample Output:
[SysAdminXpert@centos ~]$ sudo netstat -tulpn Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1197/cupsd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1394/master tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3478/sshd: osboxes@ tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1805/dnsmasq tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1193/sshd tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 1197/cupsd tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1394/master tcp6 0 0 ::1:6010 :::* LISTEN 3478/sshd: osboxes@ tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 1/systemd tcp6 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN 1995/java tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1193/sshd udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:883 0.0.0.0:* 713/rpcbind udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5353 0.0.0.0:* 740/avahi-daemon: r udp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* 1805/dnsmasq udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:67 0.0.0.0:* 1805/dnsmasq udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:68 0.0.0.0:* 961/dhclient udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* 1/systemd udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 0.0.0.0:* 722/chronyd udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:43477 0.0.0.0:* 740/avahi-daemon: r udp6 0 0 :::883 :::* 713/rpcbind udp6 0 0 :::111 :::* 1/systemd udp6 0 0 ::1:323 :::* 722/chronyd [SysAdminXpert@centos ~]$
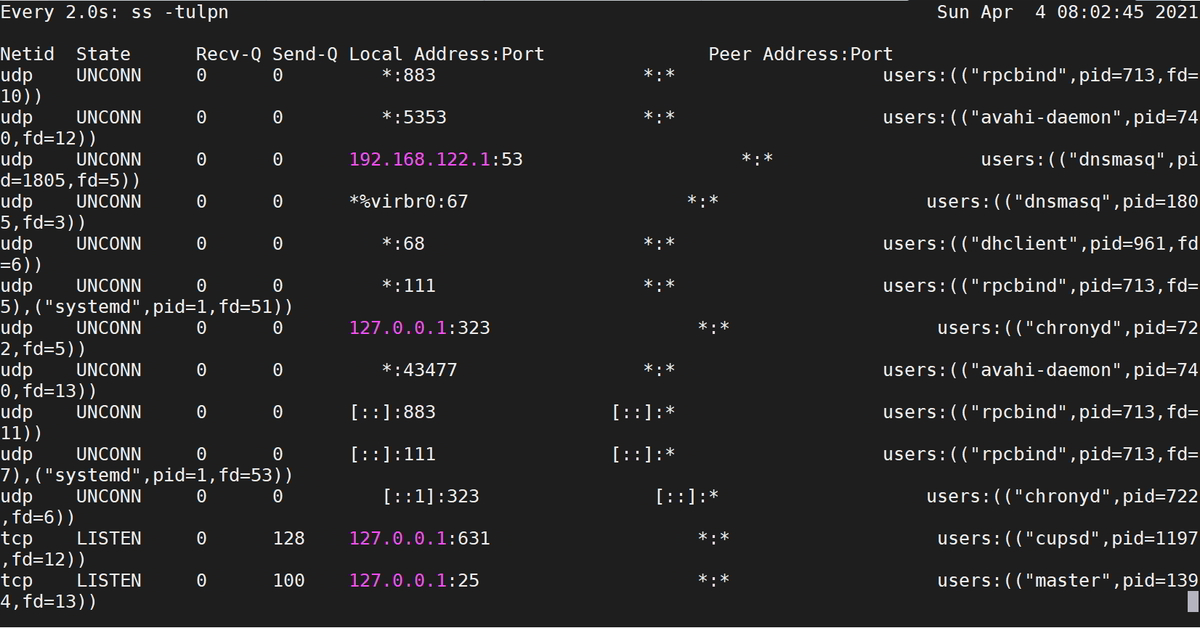
For Command ” sudo ss -tulpn “

Sample Output:
[SysAdminXpert@centos ~]$ sudo ss -tulpn [sudo] password for SysAdminXpert: Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port udp UNCONN 0 0 *:883 *:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=713,fd=10)) udp UNCONN 0 0 *:5353 *:* users:(("avahi-daemon",pid=740,fd=12)) udp UNCONN 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 *:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=1805,fd=5)) udp UNCONN 0 0 *%virbr0:67 *:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=1805,fd=3)) udp UNCONN 0 0 *:68 *:* users:(("dhclient",pid=961,fd=6)) udp UNCONN 0 0 *:111 *:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=713,fd=5),("systemd",pid=1,fd=51)) udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 *:* users:(("chronyd",pid=722,fd=5)) udp UNCONN 0 0 *:43477 *:* users:(("avahi-daemon",pid=740,fd=13)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:883 [::]:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=713,fd=11)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:111 [::]:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=713,fd=7),("systemd",pid=1,fd=53)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [::1]:323 [::]:* users:(("chronyd",pid=722,fd=6)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:631 *:* users:(("cupsd",pid=1197,fd=12)) tcp LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* users:(("master",pid=1394,fd=13)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6010 *:* users:(("sshd",pid=3478,fd=10)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:111 *:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=713,fd=4),("systemd",pid=1,fd=50)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 192.168.122.1:53 *:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=1805,fd=6)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* users:(("sshd",pid=1193,fd=3)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:631 [::]:* users:(("cupsd",pid=1197,fd=11)) tcp LISTEN 0 100 [::1]:25 [::]:* users:(("master",pid=1394,fd=14)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6010 [::]:* users:(("sshd",pid=3478,fd=9)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=713,fd=6),("systemd",pid=1,fd=52)) tcp LISTEN 0 50 [::]:8080 [::]:* users:(("java",pid=1995,fd=21)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* users:(("sshd",pid=1193,fd=4)) [SysAdminXpert@centos ~]$
In the above command, the flag:
-t – enables listing of TCP ports.
-u – enables listing of UDP ports.
-l – prints only listening sockets.
-n – shows the port number.
-p – show process/program name.
Watch Real Time TCP and UDP Open Ports
Run netstat or ss command-line tool with watch utility.
$ sudo watch ss -tulpn OR $ sudo watch netstat -tulpn
For command “sudo watch netstat -tulpn” terminal output:
To exit from the above command, press Ctrl+C.
For command “sudo watch ss -tulpn” terminal output.
End of the article, you’ve come to know how to watch real time TCP and UDP ports on Linux.