In the world of software development and continuous integration, Jenkins has established itself as a reliable and popular tool. Learn how to install Jenkins on Ubuntu 22 step-by-step with this comprehensive guide. Automate your development processes and enhance collaboration using Jenkins.
Introduction to Jenkins
Jenkins is an open-source automation server that facilitates software projects’ continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD). It enables developers to automate repetitive tasks, streamline development processes, and enhance collaboration among team members.
Prerequisites
Before you dive into the installation process, make sure you have the following prerequisites in place:
- A system running Ubuntu 22
- A user account with sudo privileges
Steps to Install Jenkins on Ubuntu 22
Updating System Packages
The first step is to ensure that your system’s package repository is up-to-date. Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Installing Java
Jenkins requires Java to be installed on your system. You can install OpenJDK by running:
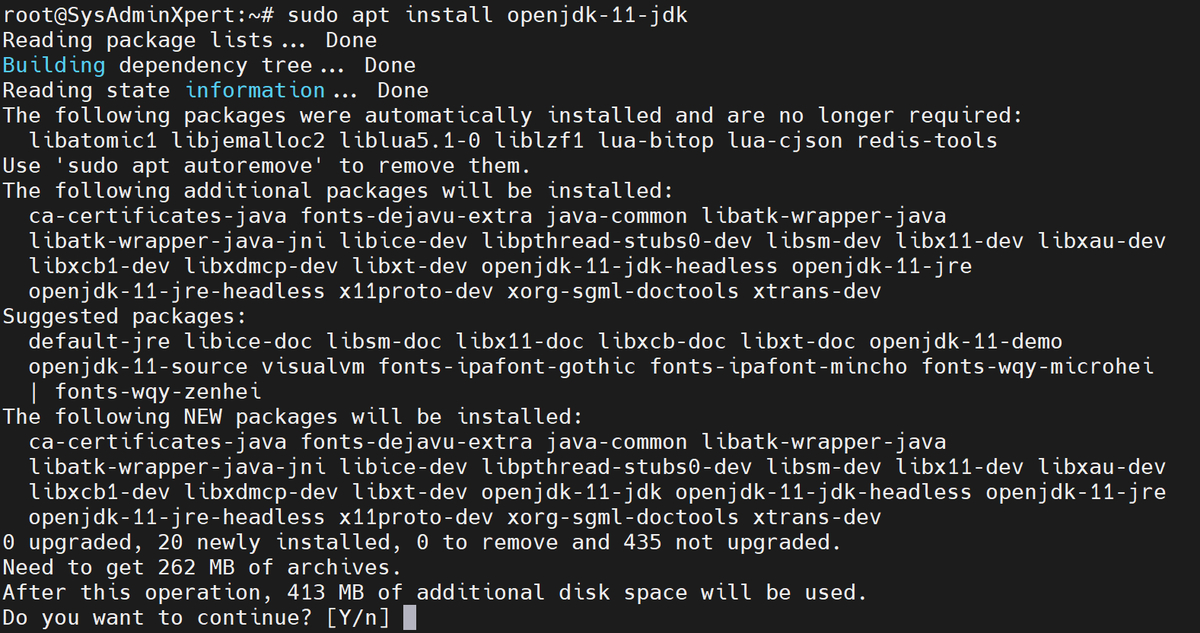
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdk
Adding Jenkins Repository
Next, you need to add the Jenkins repository to your system. This will allow you to install Jenkins using the package manager. Run the following commands:
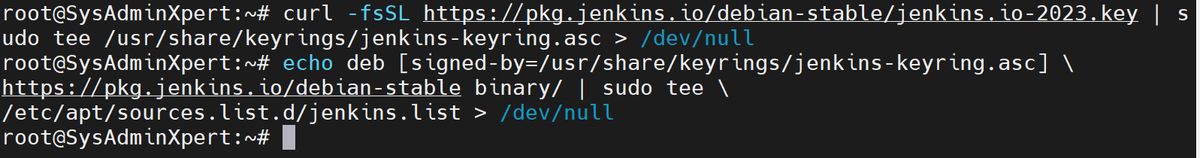
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \ /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
These above commands fetch the GPG key for the Jenkins repository, add it to the system’s keyring, and then create a new repository source entry that points to the Jenkins repository, using the downloaded GPG key for verification. This allows the system to install and update Jenkins using standard package management tools like apt.
Installing Jenkins
With the repository added, you can now install Jenkins:
sudo apt update
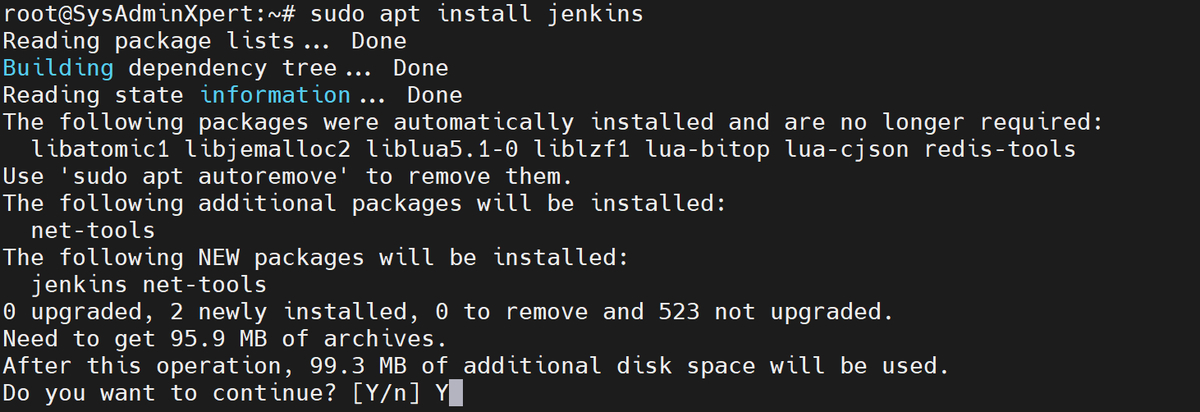
sudo apt install jenkins
Starting Jenkins Service
Once the installation is complete, start the Jenkins service and enable it to start on boot:
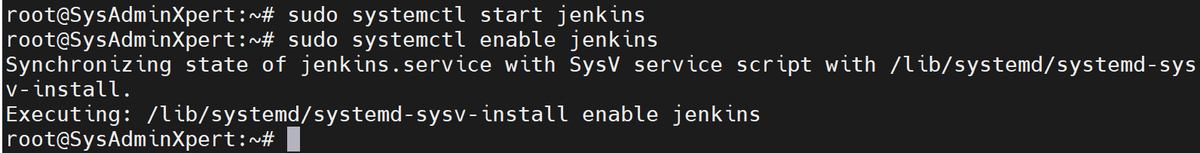
sudo systemctl start jenkins sudo systemctl enable jenkins
Accessing Jenkins Web Interface
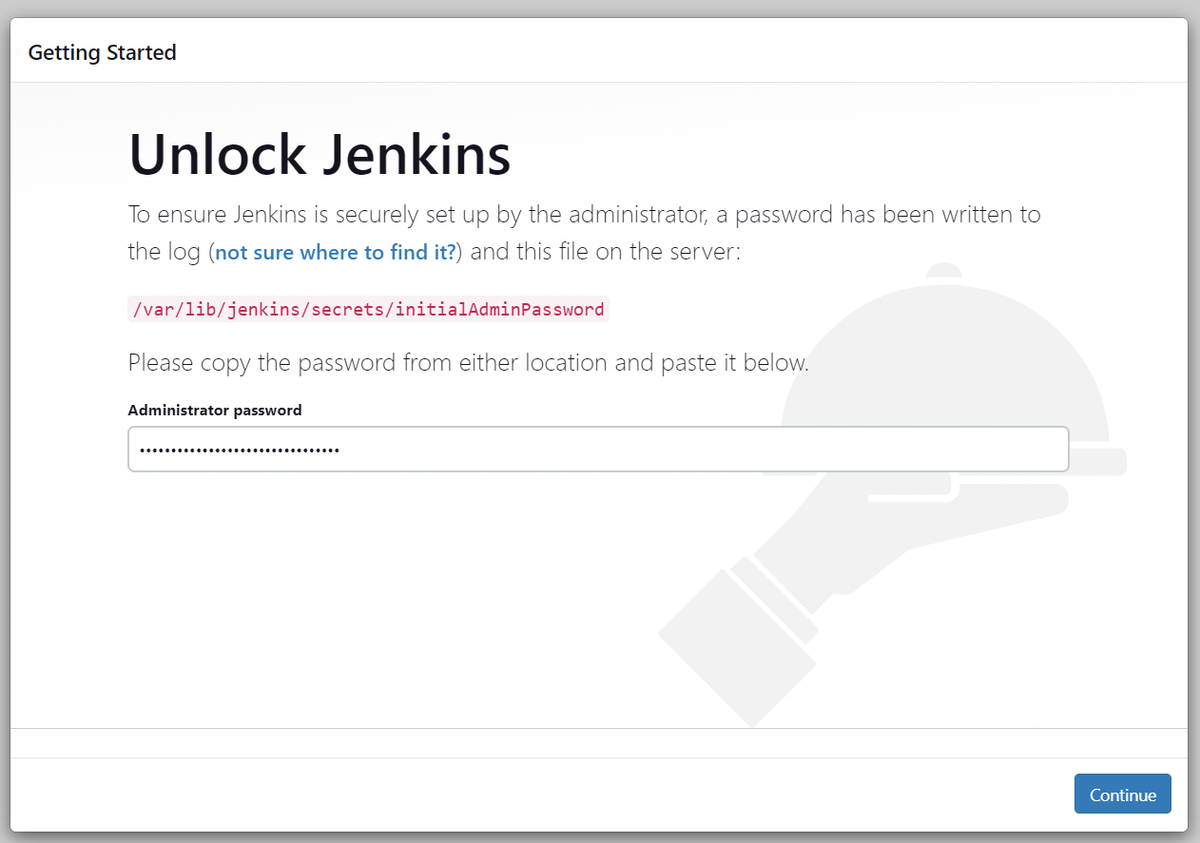
You can access the Jenkins web interface by opening your browser and navigating to http://your_server_ip_or_domain:8080. You will be prompted to enter the initial admin password, which you can find on your server:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
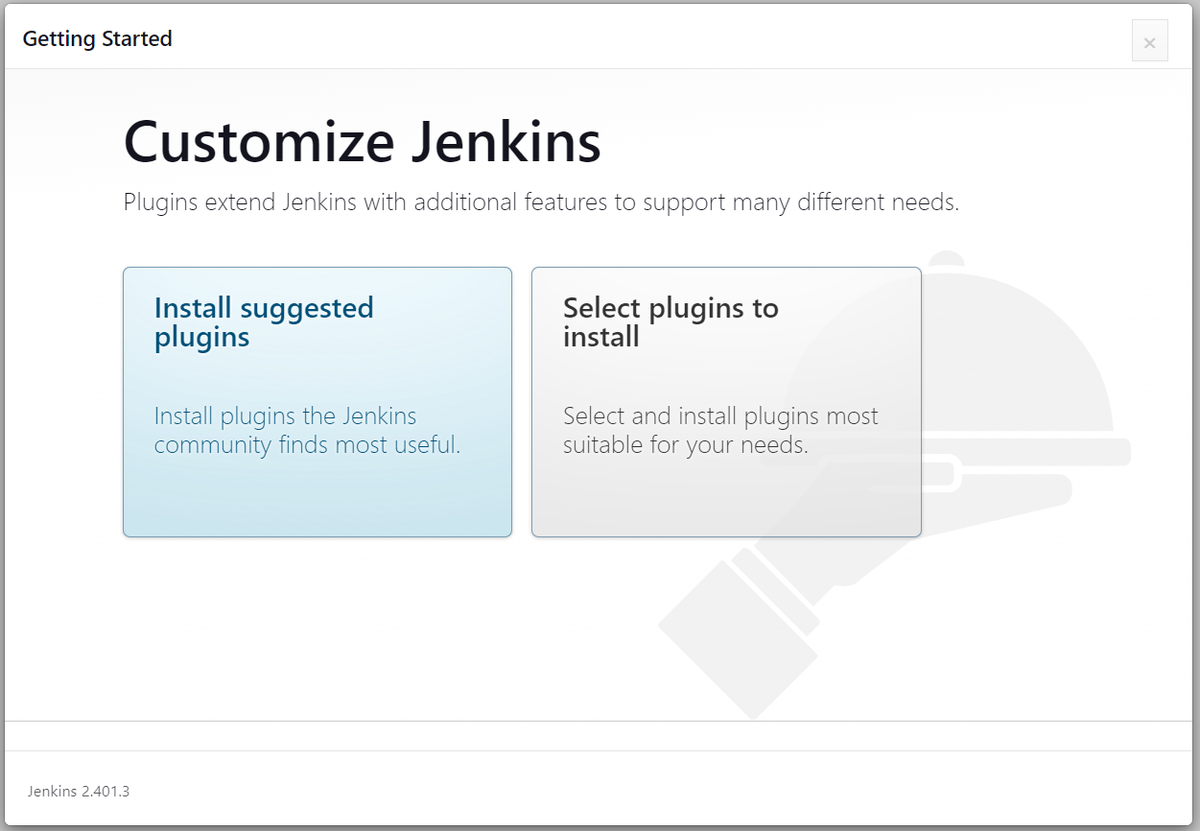
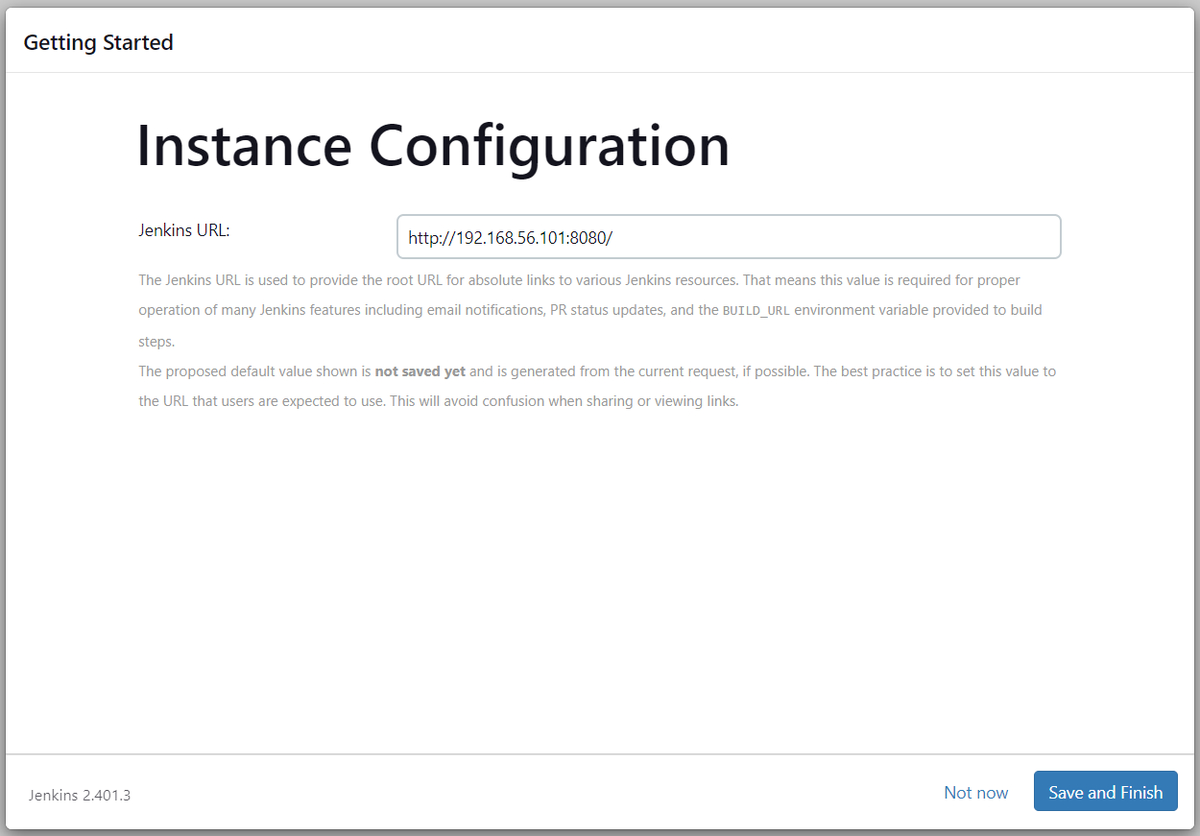
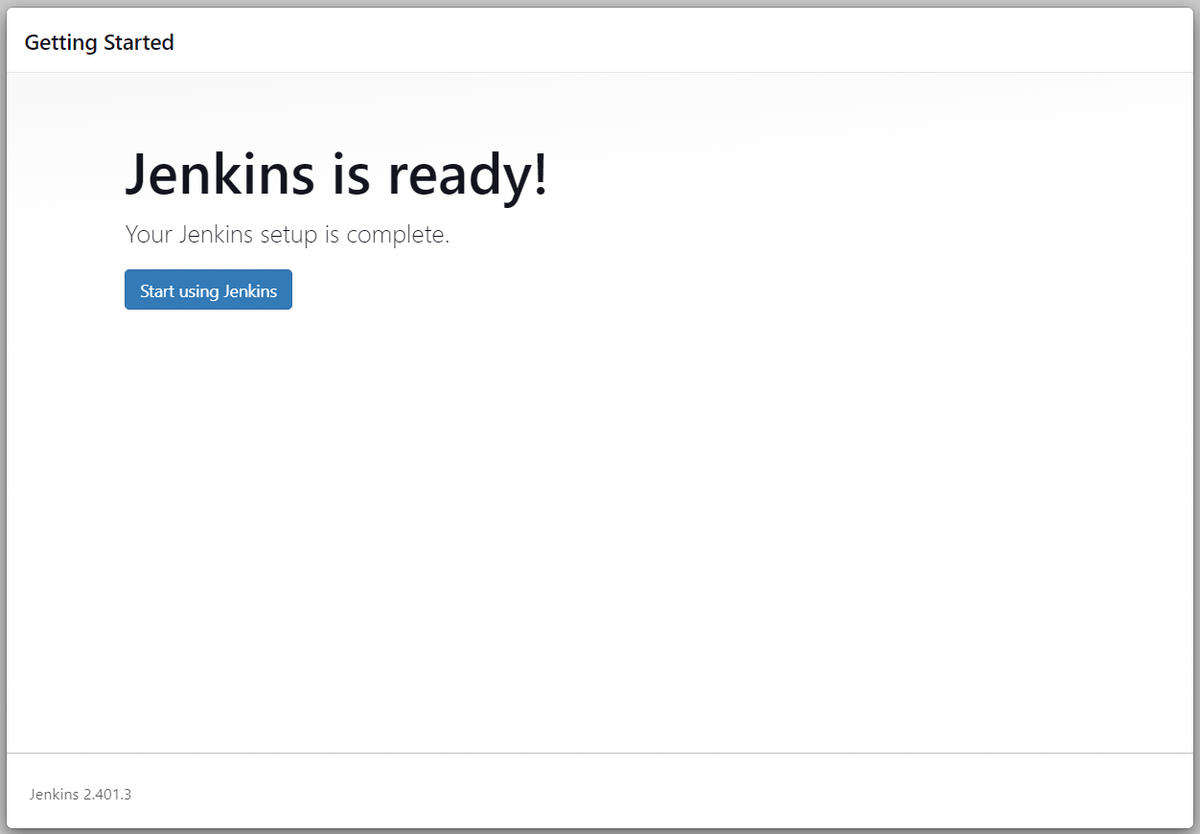
Setting up Jenkins
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the Jenkins setup process. You can choose to install suggested plugins or select specific ones based on your requirements.
Creating Your First Jenkins Job
Once the setup is complete, you can start creating your first Jenkins job. Click on “New Item,” give your job a name, and choose the type of job you want to create (e.g., Freestyle project or Pipeline).
Jenkins Plugins
Jenkins offers a wide range of plugins that enhance its functionality. You can browse and install plugins by navigating to “Manage Jenkins” > “Manage Plugins.”
Securing Jenkins
It’s crucial to secure your Jenkins installation to prevent unauthorized access. You can configure security settings, manage user accounts, and enable authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Uninstalling Jenkins
If you ever need to uninstall Jenkins, you can do so by running:
sudo apt remove --purge jenkins
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Encountering issues is not uncommon during software installations. Refer to the official Jenkins documentation and online resources to troubleshoot common problems.
Conclusion
Installing Jenkins on Ubuntu 22 can significantly improve your development workflow by automating tasks and streamlining collaboration. By following this guide, you’ve successfully set up Jenkins and are ready to embark on a more efficient development journey.
FAQs
Q1: Can I install Jenkins on other Linux distributions?
A: Yes, Jenkins can be installed on various Linux distributions, but the installation process might differ slightly.
Q2: How do I reset the Jenkins admin password?
A: You can reset the admin password by accessing the server’s terminal and using the resetAdminPassword command.
Q3: Can I use Jenkins for non-Java projects?
A: Absolutely! Jenkins supports projects developed in various programming languages.
Q4: Is it necessary to install all suggested plugins?
A: It’s not mandatory, but installing suggested plugins can enhance Jenkins’ capabilities.
Q5: Can Jenkins be used for manual testing processes?
A: Yes, Jenkins can be configured to facilitate manual testing and approval processes within a CI/CD pipeline.
See also:
Top 20 Jenkins Best Practices for Efficient and Secure CI/CD Workflows
How To Install Jenkins on Rocky Linux 8 or CentOS 8
How to Install Jenkins on CentOS 7 or RHEL 7
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery
How to run Jenkins on Port 80 in Linux
How to Get Started with DevOps in 5 Easy Steps
10 Essential DevOps Tools for Your Business: Automate and Streamline Your Workflow